Let’s clear up the confusion. In this guide, we’ll break down the fundamentals of drug dissolution testing, highlight the key pump features to prioritize, and show how Fluid Metering’s solutions can help you design a dissolution tester that delivers consistent, high-quality results.
What is Drug Dissolution?
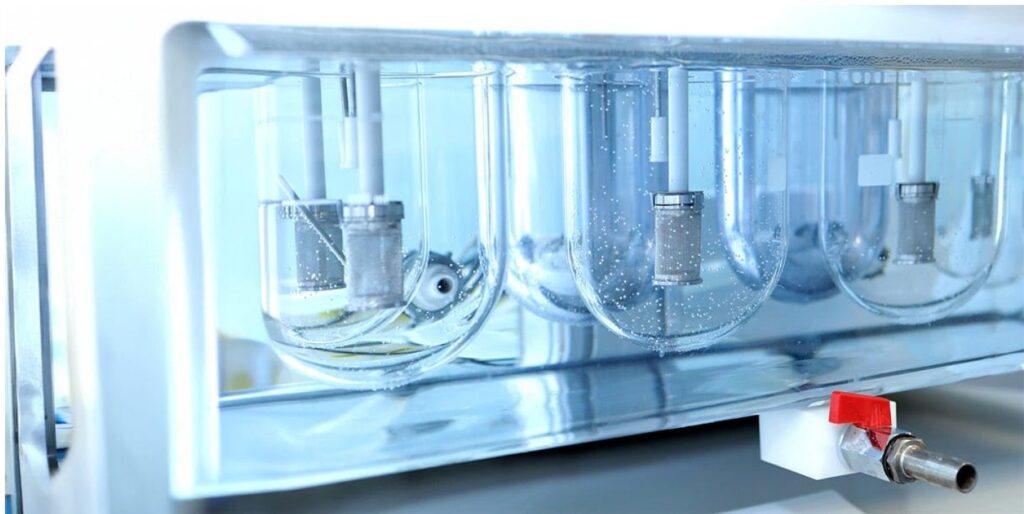
Drug dissolution is a critical process in pharmaceutical development that measures how quickly an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is released from a solid dosage form—such as a tablet or capsule—into a liquid medium. This rate of release directly impacts how the drug is absorbed in the body, influencing its bioavailability, therapeutic effectiveness, and overall safety for the patient.
Dissolution testers are designed to simulate the environment of the human stomach, allowing researchers to evaluate how long a drug remains active and how efficiently it is absorbed. These systems are also essential for quality control, ensuring that each tablet or capsule performs consistently—batch after batch—to deliver reliable therapeutic outcomes.
Types of Drug Dissolution Testing
- Immediate-Release Dissolution
- Measures how quickly an immediate-release drug dissolves in the stomach and is available for absorption.
- Used for fast-acting drugs, like painkillers or fever reducers.
- Extended-Release (Controlled-Release) Dissolution
- Evaluates how a drug gradually releases over time, ensuring a sustained therapeutic effect.
- Used for long-acting medications with reduced dosing frequency.
- Delayed-Release Dissolution
- Examines drugs that bypass the stomach and dissolve in the intestines.
- Used for enteric-coated tablets, which protect the drug from stomach acid.
- USP Apparatus-Based Dissolution Testing
- Uses standard United States Pharmacopeia (USP) dissolution apparatus to simulate drug release conditions:
- USP 1 (Basket Method): Drug is placed in a rotating basket submerged in a liquid medium.
- USP 2 (Paddle Method): Drug is stirred in the medium using a paddle.
- USP 3 (Reciprocating Cylinder): Mimics drug release in changing pH conditions (ideal for extended-release drugs).
- USP 4 (Flow-Through Cell): Continuous flow system ideal for poorly soluble drugs.
- Uses standard United States Pharmacopeia (USP) dissolution apparatus to simulate drug release conditions:
- Biorelevant Dissolution Testing
- Uses simulated fluids like gastric juices to mimic real physiological conditions.
- Helps predict how the drug behaves in the human body under different conditions.
What Pump Specifications Should an Engineer Look For?
When choosing a pump for drug dissolution testing, several key specifications should be prioritized to ensure accurate and consistent performance:
- Flow Rate Control: The pump should allow for adjustable flow rates while maintaining a consistent pulse count. This ensures smooth, uninterrupted fluid delivery throughout the test cycle.
- Chemical Compatibility: The pump must be resistant to a wide range of substances commonly used in dissolution testing, including water, hydrochloric acid (HCl), simulated gastric fluids, pepsin, bile salts, buffering agents, and various organic solvents.
- Reliability and Efficiency: Precision and repeatability are essential. The pump should deliver stable flow rates even at low volumes and be durable enough to withstand continuous operation and repeated use without degradation in performance.
Which Pumps Meet the Criteria?
Fluid Metering’s CeramPump® valveless piston technology features a rotating, reciprocating ceramic piston that delivers long-term, drift-free fluid control—without relying on check valves. This design ensures exceptional reliability and precision, making it ideal for the demanding requirements of drug dissolution testing.
In many cases, traditional pump systems require up to 300 individual fluidic components within a dissolution tester. This complexity increases maintenance demands and long-term operational costs. By contrast, Fluid Metering’s FENYX™ Variable Dispense Pump simplifies the fluidic architecture, reducing the number of components to around 30. It eliminates the need for syringes, priming pumps, excess tubing, fittings, and other auxiliary parts.
FENYX™ also replicates stomach-like conditions by maintaining a constant motor speed while adjusting flow rate via a linear actuator. Competing systems often lack this capability, forcing OEM engineers to either purchase additional hardware or invest significant time and resources into developing a custom solution.
Solving the Drug Dissolution Dilemma
At Fluid Metering, we understand the complexities involved in designing effective drug dissolution testers. That’s why we offer expert engineering support to help OEM developers choose the ideal pump for their specific application needs.
Let us help you simplify your system, improve accuracy, and reduce long-term costs.
Contact us today to find the right solution for your drug dissolution challenge!