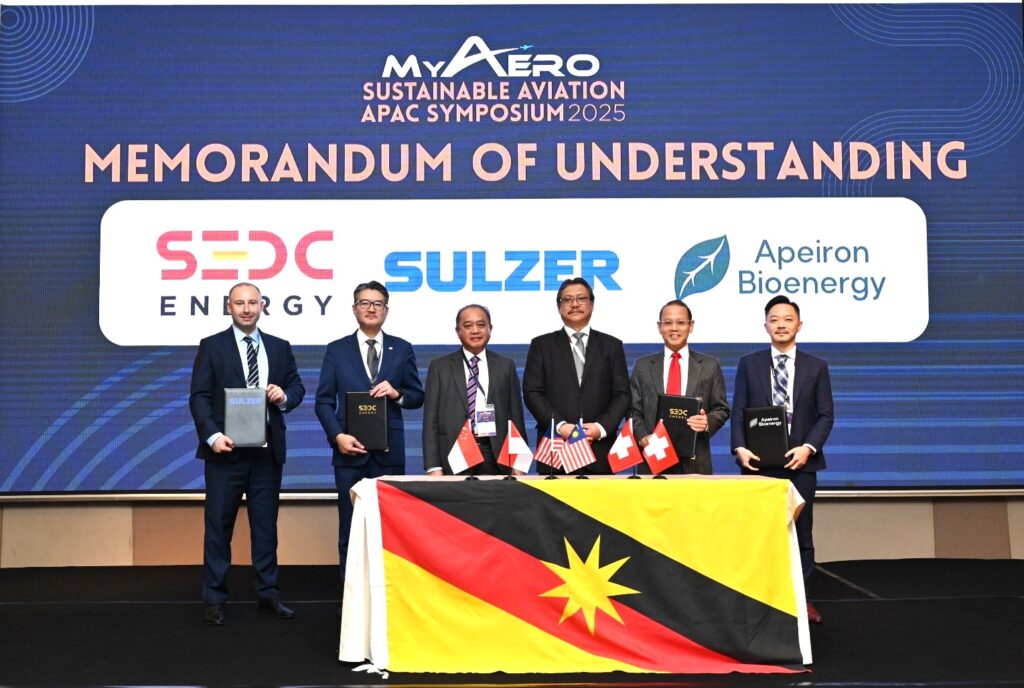
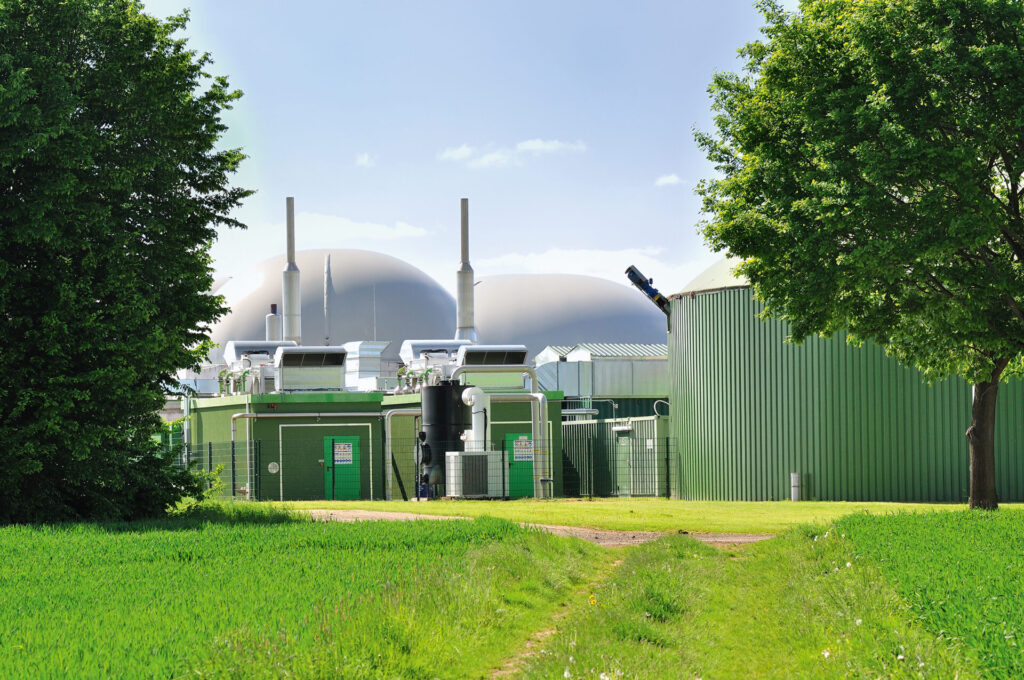
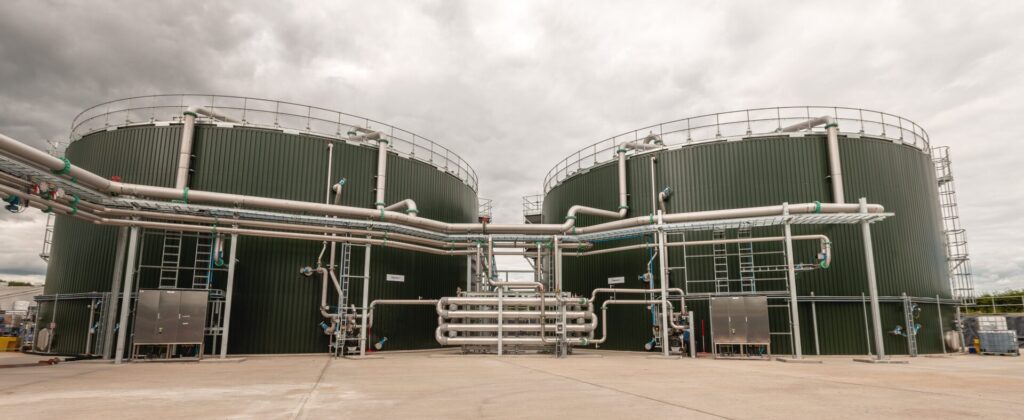
Biogas processing is the method of converting organic waste materials, such as agricultural residues and food waste, into renewable energy through anaerobic digestion. This biological process breaks down organic matter in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas primarily composed of methane, which can be used for electricity generation, heating, or as vehicle fuel.
How does anaerobic digestion work in biogas processing?
Anaerobic digestion involves several stages: hydrolysis, acidogenesis, acetogenesis, and methanogenesis. During these stages, microorganisms break down organic materials into simpler compounds, ultimately producing biogas. This process not only generates energy but also minimizes waste and reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
What are the benefits of biogas processing?
Biogas processing offers numerous benefits, including sustainable waste management, renewable energy production, and reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. It helps divert organic waste from landfills, provides a renewable energy source, and produces digestate, a nutrient-rich fertilizer that can enhance soil health.
What materials can be used in biogas processing?
A wide range of organic materials can be utilized in biogas processing, including agricultural residues (such as crop leftovers), food waste, manure from livestock, sewage sludge, and certain industrial wastes. This versatility makes biogas an effective solution for various sectors, from agriculture to municipal waste management.
How is biogas processed for energy use?
Once produced, biogas can undergo purification processes to remove impurities like carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide, resulting in Renewable Natural Gas (RNG). This refined biogas can then be injected into natural gas pipelines, used for electricity generation, or converted into compressed natural gas (CNG) for vehicles, making it a versatile energy source.