Preliminary treatment
Preliminary treatment is the removal of coarse solids and other large materials often found in raw wastewater.
Primary treatment
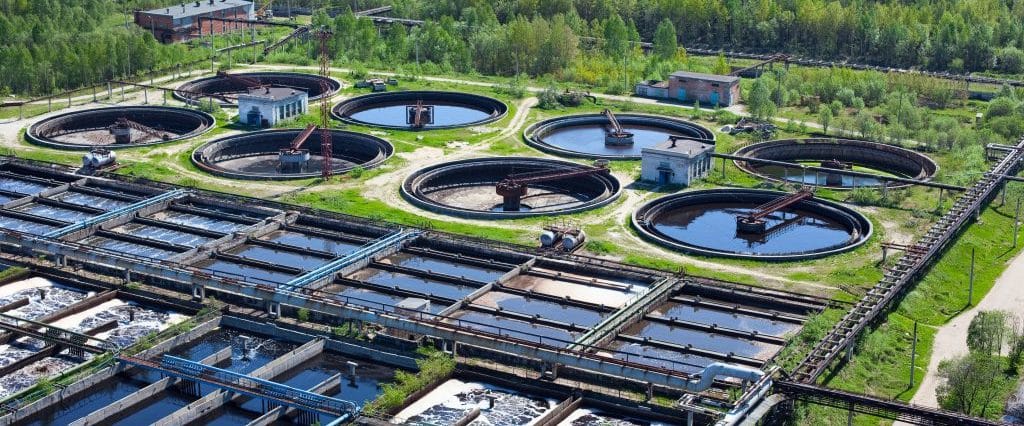
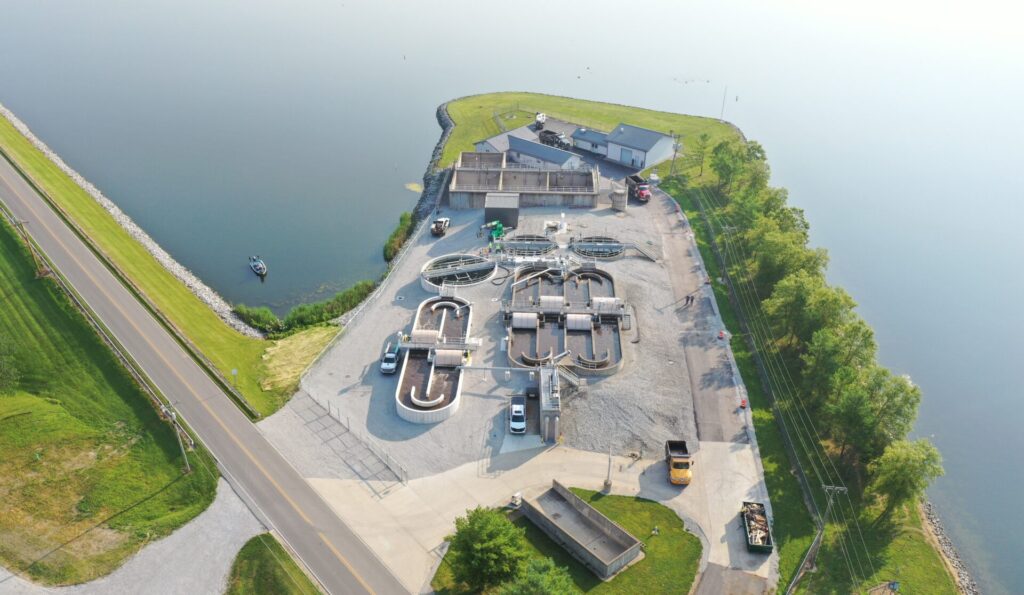
Primary treatment is the removal of settleable organic and inorganic solids by sedimentation, and the removal of materials that will float (scum) by skimming.
Secondary treatment
Secondary treatment is the further treatment of the effluent from primary treatment to remove the residual organics and suspended solids. Secondary (or biological) treatment uses microbes to consume dissolved organic matter that escapes primary treatment, converting it to carbon dioxide, water and energy for microbe growth and reproduction.
Advanced treatment
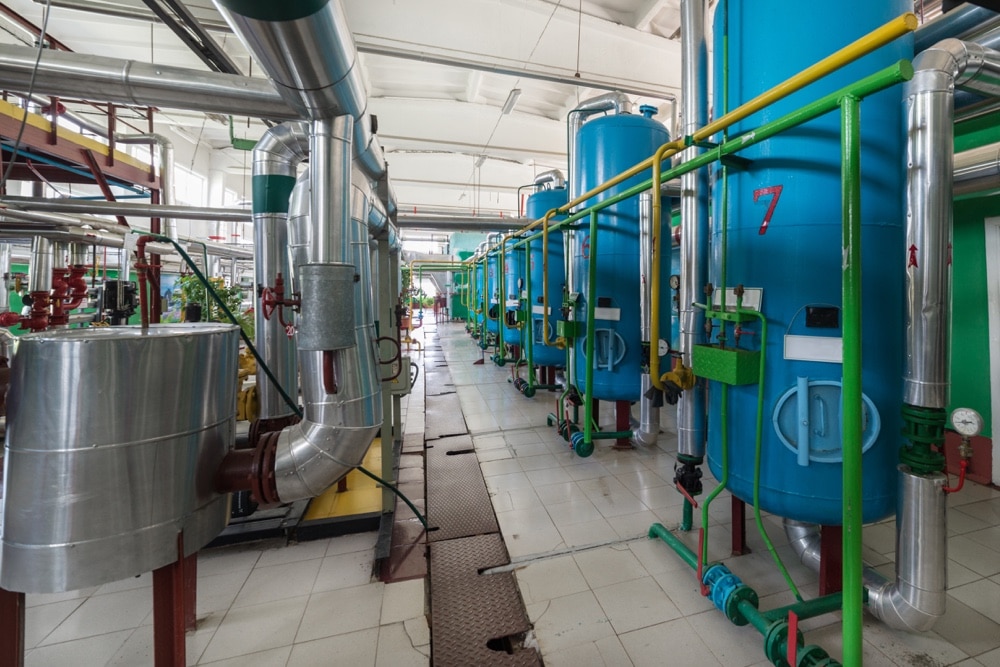
Advanced wastewater treatment is employed when specific wastewater constituents which cannot be removed by secondary treatment must be removed. To eliminate specific contaminations to meet regulatory requirements, many plants must resort to special treatment, e.g., the Fenton process to remove non-biodegradable COD.
Disinfection
After the primary treatment stage, the secondary treatment process and advanced treatment process, there are still some diseases causing organisms in the remaining treated wastewater. To eliminate them, the wastewater must be disinfected in tanks that contain a mixture of chlorine and sodium hypochlorite.
Sludge Treatment
The sludge that is produced and collected during the primary and secondary treatment processes requires concentration and thickening to enable further processing.