Of course, this also increases the MCR effort required to squeeze production into tighter and tighter process schedules. Phoenix Contact’s new pluggable test disconnect terminals now simplify servicing and maintenance.
In the chemical and process industries, many new approaches designed to make production quicker, cheaper, and more flexible have been tested in the last few years – and quite successfully so. This has allowed the industry to recover relatively quickly after the 2009 crisis. The success was due not only to container solutions and modularization, but also retrofitting and system expansion.
These tendencies have also facilitated the increased use of HART (Highway Addressable Remote Transducer) protocol-capable sensors and control valves. This technology uses the classic 4-20 mA current loop as a transmission medium for a modulated data transmission signal in accordance with the Bell 202 FSK standard, in which communication is conducted by means of signal sequences of varying frequencies alternating between command and response on simple twisted-pair cables. This keeps down implementation costs, and the actual analog measurement signal remains unaffected. In this way, multiple variables or pieces of information can be transmitted, and remote diagnosis or device configuration can be carried out.
What are disconnect terminals for?
HART is used with a number of sensors for measuring temperatures, pressures, vacuums, filling levels, distances, conductivities, densities, and pH values. Valves, servo-motors, inputs and outputs of all kinds, and analog values are also controlled using HART. This can be done in three ways:
- Readjustment and calibration of measurement values
– does a temperature sensor output measurement reading coincide with the reference voltage, for example? - Troubleshooting in complex systems
– does a filling level or proximity sensor actually emit a signal when the target level is reached? - Parameterization or querying of device configurations using a computer
It is often necessary to connect measuring or diagnostic devices to a current loop – for test measurements of the parameters received by the sensors on the one hand, and for evaluation of the switching states or system parameters on the other. In conventional control systems, i.e., where no current loop is used for data communication, a short signal interruption does not necessarily cause any problems. But if the current loop is also the transmission medium, interruption causes communication with the HART modem to be broken off and a system error message to be sent. That is why interruption-free connection is indispensable for HART-controlled systems.
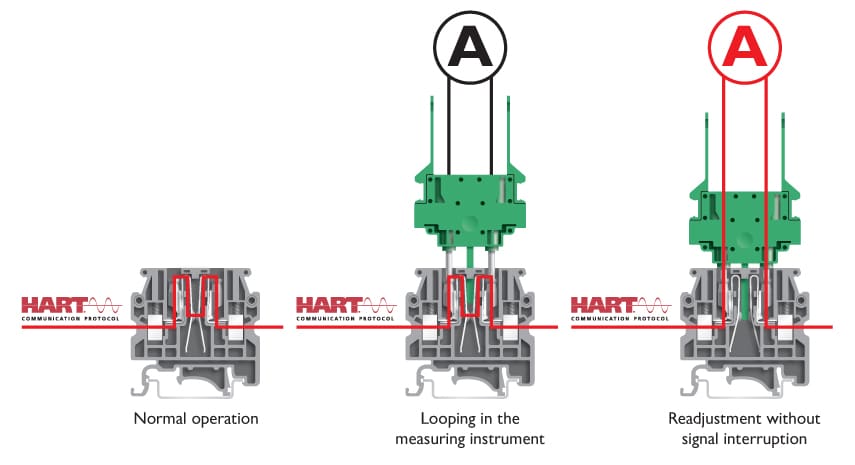
The classic disconnect terminal normally has test sockets on each side of the disconnect point into which the measuring device is plugged before the disconnect knife is opened, which must be done if a test measurement is to be made. The new UK 4-SD product line from Phoenix Contact makes that easier because the base terminal’s disconnect zone is designed as a contact spring . The contact zone is automatically disconnected when a suitable test disconnector is plugged in. The length of the green plug’s disconnect reed ensures that capacitive contact is made with the contact sockets. This facilitates safe, interruption-free connections so that HART communication is not impaired by the measurement process.
Reduce downtime
The advantages of a pluggable disconnect terminal are obvious. First, any signal that is conducted through such a terminal can be easily evaluated by means of a quick plugging-in of the test disconnector. This is particularly convenient during troubleshooting. When technicians are working with conventional disconnect terminal blocks, they must ensure that the testing lines are securely plugged in and do not slip out. Testing lines also often impair the opening and closing of the disconnect knife. The UK 4-SD disconnect terminal, whose part width is only 6.2 mm and length only 45.5 mm, can be installed and operated even in compact boxes within the system.
It is also advantageous that error messages that would otherwise arise due to the interruption of the HART protocol are avoided. Such messages would consume a great deal of time and take up unnecessary space in error logs. Finally, responses can be conveniently read out or tested at the test disconnect terminals by means of suitable analysis and diagnostic devices.
Eliminate errors and calibrate measurement readings
Despite the simple bus topology, system faults may still necessitate repeated service calls. During such calls, it is important to have quick, easy access to the signals by means of multimeters, diagnostic tools, and current loop profile calibrators. Common causes of faults include:
- Substandard connections or corrosion at the connection point in the complex system structure – resulting in inaccurate measurement values.
- Overloaded 24 V voltage supplies, leading to an undefined sensor or actuator signal state.
- Incorrectly interpreted input and output signals that disrupt the process.
- Noisy measurement signals from the signal transmitters that make it difficult to adhere to process schedules.
The pluggable UK 4-SD disconnect terminal represents a well-tested technology: The clamping sleeve’s Reakdyn design ensures a self-locking screw connection. The clamping sleeves are nickel-plated and the contact springs silver-plated for stable, low transition resistances. The spring’s base material is a hard copper alloy – the surface is passivated and greased to better protect it against corrosion. The disconnect terminal product line is also shock- and vibration-tested according to DIN EN 61373, with a Category 1B certification. The terminal withstands salty atmospheres according to DIN EN 60068-2-11 with a test duration of 144 hours, as well as atmospheres containing sulfur dioxide according to DIN EN 50018.
Test plug defines switching behavior
In order for the product line to address all switching behaviors of a disconnect terminal, Phoenix Contact has made three test disconnectors available in different colors (Figure 4), allowing either capacitive (red) or delayed (green) disconnection based on the differences in their disconnect reeds. For a simple disconnection procedure, there is the service disconnection plug, which does not provide any power pick-off terminals (gray). Another plug, which merely contacts the test sockets without disconnecting and is suitable for reading out HART signals, is currently in planning. Snapping together multiple-pin blocks, thus creating simple wire jumpers, also makes it possible to construct suitable circuits for use with current and capacitor voltage transformers. This allows current transformers to be capacitively short-circuited. With currents of up to 16 A/500 V and a maximum of 6 mm² clamping capacity, the UK 4-SD product line covers a large portion of process engineering requirements. Where currents of up to 30 A may occur, a more powerful product line can be called upon – which again features inline test disconnectors.
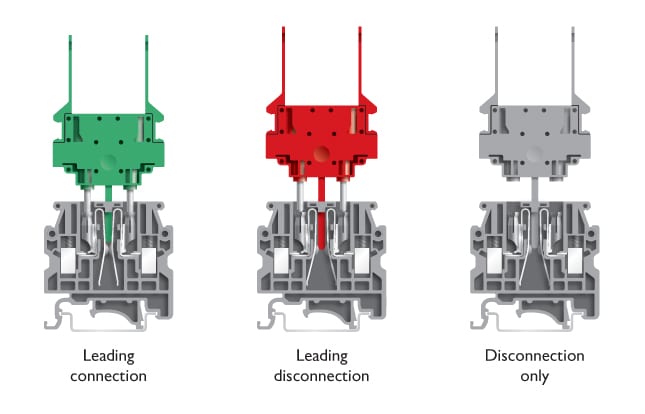
Pluggable disconnecting
Pluggable disconnect terminals simplify service and maintenance work by providing the following functions:
- Interruption-free connection
- Safe disconnecting before contacting the test sockets
- Simple disconnect function
- Multiple-pin parallel switching operations by means of inline test plugs
These functions make pluggable disconnect terminals eminently suitable for maintenance-intensive system concepts involving frequent adjustment work.































